
It's been a long since I wrote a blog so I thought let's try something not everyone talks about. The Importance of Best Practices and Design Principles for a Web Developer. This will be my first blog regarding backend development. Let's get Started...
What the Heck is MVC?
First of All, MVC stands for Model-View-Controller. A certain set of rules/principles for maintaining your Code Structure is quite popular in Backend Development. It suggests separating our file structure into three parts and dividing the logic of our app by its utility.
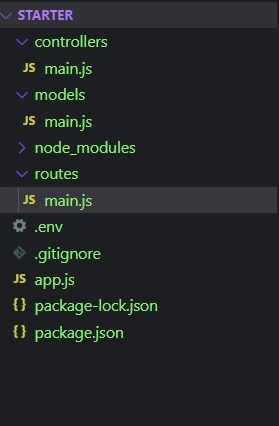
Now let's dig deep into each one of them.
1. MODEL
The Model contains the Schema of your app which can be defined by any ORM (Object Relational Mapper) or ODM (Object Document Mapper) of your choice. The sole purpose of a Model is to interact (query/store) with the Database from your App.
Basically storing your app data in a database with the help of Schema (the structure in which the data should be stored) generation is done by the Model Files.
2. View
The user doesn't care about what your app does behind the scenes. He only cares about the data it receives when it sends a Request to the server.
The View files are primarily your HTML, CSS and JS files but can also contain other static files like Videos, Images or any Other Text or Media files. In Node JS Express Framework, these files go into the Public folder which gets delivered to the Browser by the Server as a response whenever a certain request is made. The general purpose of our Views is to display the data in a user friendly manner to the Client (Web Browser).
3. Controller
This is what Controls the main business logic of our App. While using NodeJS, we refer to these as Routes files. It basically works as the thread between our Models and Views. It stores and retrieves data from and to our Models and sends the data to the Views to send it back to the Client.
In an Express environment, these files work on the principles of taking a request from our Views and sending data as a response to the user.
We can also extract the logic of these files in a separate Controller file which processes all the computation and logic of our app. This is basically a good Coding practice to keep our code concise, clean and Reusable.
In the below snippet, our Route File runs the Controller function called Login and Returns data whenever our login API endpoint gets hit.
I hope this blog gave you some basic Ideas of the practical meaning of the MVC architecture and what should be your approach for structuring a new Express App.
Until Next Time...
Happy Debugging Coding👋